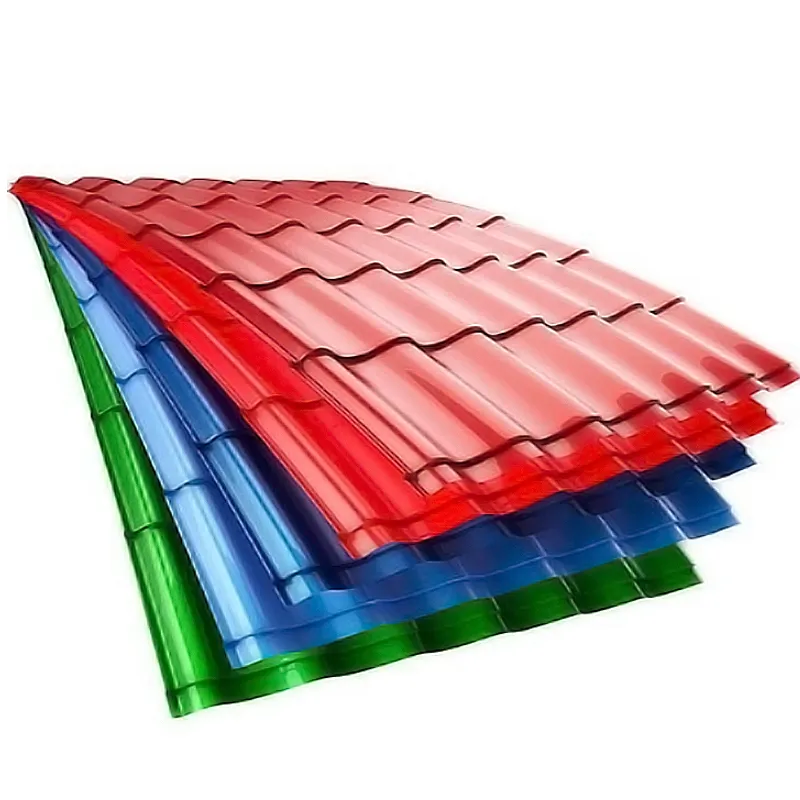
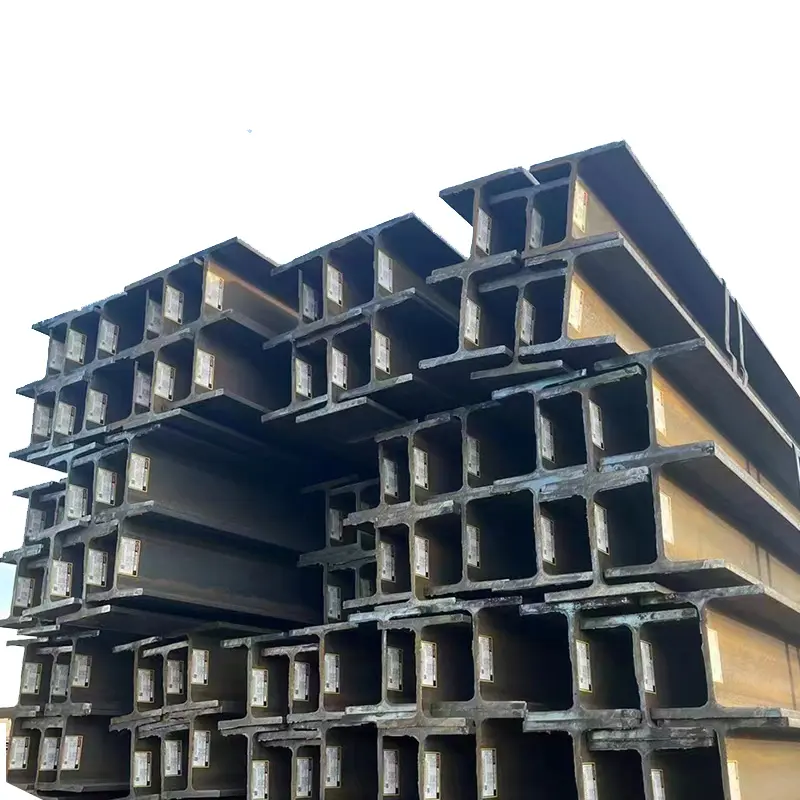
Weldable carbon steel plates are specifically designed to facilitate various welding processes—such as shielded metal arc welding (SMAW), gas metal arc welding (GMAW), and flux cored arc welding (FCAW)—without compromising mechanical properties or causing excessive distortion or cracking. Key to their weldability is controlled chemical composition, particularly low carbon content (typically ≤0.25%) and limited sulfur/phosphorus impurities, which reduce the risk of hydrogen induced cracking and brittleness. Alloying elements like manganese are added to improve strength while maintaining weldability, and deoxidizers such as silicon or aluminum ensure a clean weld pool. Weldable carbon steel plates may undergo normalizing or annealing to achieve a uniform microstructure and reduce residual stresses. Preheating and post weld heat treatment (PWHT) requirements depend on plate thickness and welding parameters, with thicker sections often requiring preheating to slow cooling rates and prevent martensite formation. Mechanical properties after welding must meet or exceed base metal specifications, with tensile tests, bend tests, and impact tests conducted on welded joints to ensure integrity. These plates are widely used in construction (welded steel frames), pressure vessels, pipelines, and structural components where reliable welds are essential. Standards like ASTM A516 for pressure vessel plates or EN 10149 for high strength structural steel define weldability requirements. Proper selection and welding procedures are critical to ensuring the structural safety and longevity of welded components.